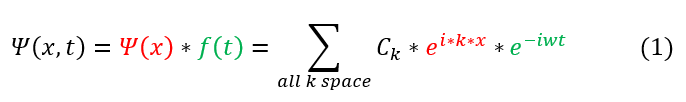Mind Network - Samuel Solomon
Scatter States
A Touch on Dispersion
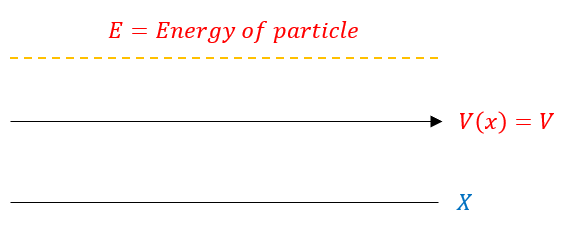
Lately, we have focused our quantum discussions on particles going through potentials; however, not all particles face such a barrier. Sometimes, particles have enough energy so that they can surmount all potential barriers (they can classically access every location). We call these systems scatter states as the particle can scatter over the potential barrier.
Let us start our discussion of stater states with the most simple example:
Let us start our discussion of stater states with the most simple example:
To the careful examiner, this example may remind people of free particles (where V(x) = 0). In fact, a free particle is an example of scatter states (and we already know how to handle those).
We can remember that the solution to the free particle is the following:
We can remember that the solution to the free particle is the following:
Where psi(x) is the time independent form of the wave function and is composed of different basis functions e^ikx.
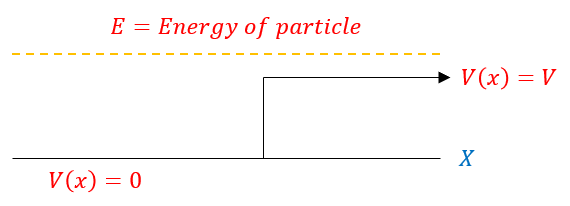
All of this was very simple. The problem is, not all scatter states resemble a free particle. Sometimes, the potential is split into two functions:
All of this was very simple. The problem is, not all scatter states resemble a free particle. Sometimes, the potential is split into two functions:
Why is this important, one may ask? Well to answer this question one must remember a little bit of wave mechanics. A wave function is composed of different basis waves. While we observe the wave function (the wave packet) move throughout space, it is really the basis functions (which sum up to the wave function) that are moving. Think about Fourier transforms. One can create a square wave out of an infinitesimal sum of sinusoidal functions. While one may see the square translate in space, physically, it is really the sinusoidal basis waves that move. This means, as physicists, we need to keep track of two different wave properties:
1. Phase velocity: the wave velocity of the basis functions that make up the wave
2. Group velocity: the wave velocity of the total wave function (the envelope of the wave; psi(x,t))
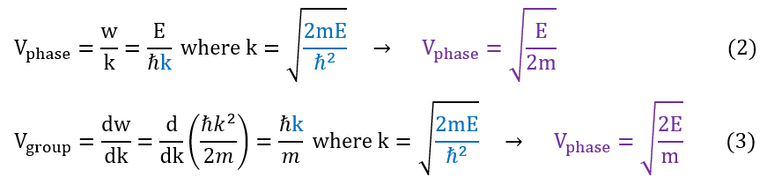
Sometimes, the phase velocity and the group velocity are out of sync with each other. Physically, this results in a phenomenon known as dispersion. For this course, let us build up these implications using the following wave mechanics formula (for simplicity sake, I will again use the free particle; V(x)=0):
1. Phase velocity: the wave velocity of the basis functions that make up the wave
2. Group velocity: the wave velocity of the total wave function (the envelope of the wave; psi(x,t))
Sometimes, the phase velocity and the group velocity are out of sync with each other. Physically, this results in a phenomenon known as dispersion. For this course, let us build up these implications using the following wave mechanics formula (for simplicity sake, I will again use the free particle; V(x)=0):
While wave dispersion is a super interesting topic on its own, it is actually not required to understand scatter states. Nevertheless, I do want to take out a very important principle about the equation. Wave velocities are a function of the particle's energy. Specifically (generalizing out of free particles), it is a function of the energy-potential gap.
Waves also do not enter boundaries all at once. Rather, a little part of the wave enters first and changes speed. Then a little more enters and also changes speed. Each basis function changes speed based on its own energy-potential gap. This leads to a dispersion effect (the wave packet spreads out). We have so far ignored this wave property, but as the energy-potential gap changes, so does the 'k' value, the particle's energy, and the particle's momentum.
Another thing to note about scatter states is that, because each basis state has its own energy, while some basis sets may indeed scatter over the potential well, some basis sets may just tunnel in and reflect back (if you throw a ball at the wall, it can either go through or bounce back depending on the energy of the ball).
Waves also do not enter boundaries all at once. Rather, a little part of the wave enters first and changes speed. Then a little more enters and also changes speed. Each basis function changes speed based on its own energy-potential gap. This leads to a dispersion effect (the wave packet spreads out). We have so far ignored this wave property, but as the energy-potential gap changes, so does the 'k' value, the particle's energy, and the particle's momentum.
Another thing to note about scatter states is that, because each basis state has its own energy, while some basis sets may indeed scatter over the potential well, some basis sets may just tunnel in and reflect back (if you throw a ball at the wall, it can either go through or bounce back depending on the energy of the ball).
|
|
|