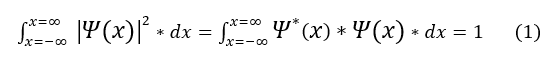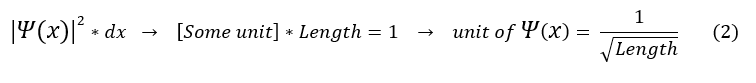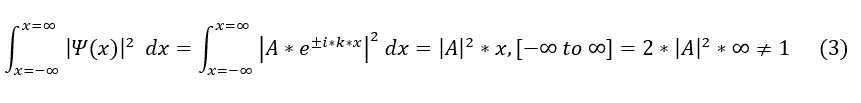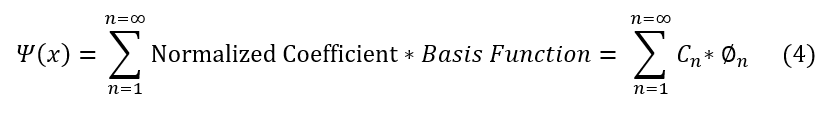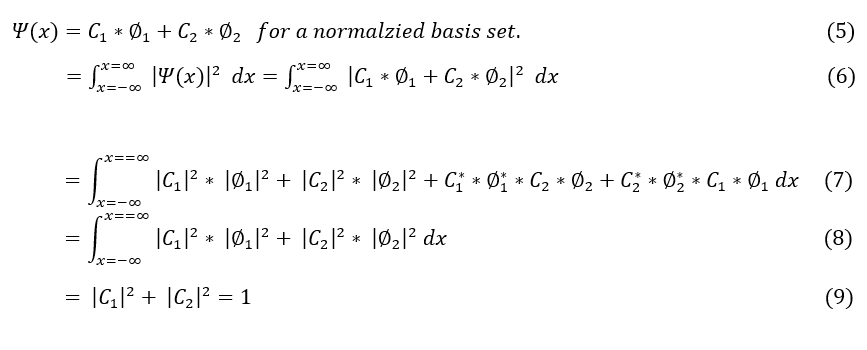Mind Network - Samuel Solomon
Problems with the Wave Function
Now that I have introduced the concept and the motivation for the wave function, let us all now exhale and agree that the wave function is a poor man’s attempt at a description of matter. LITERALLY! All I did was slap the wave function on the last page, after motivating the wave-like nature of particles, but I have already proven to you that matter is not a wave and hence not actually described by the wave function. It is important to remember this because it is this reason that the wave function has no physical meaning.
Now that the ranting is done, let us see how we can and cannot use this un-physical wave function. We will tackle this by defining our first quantum mechanical postulate (unproven good guesses):
Now that the ranting is done, let us see how we can and cannot use this un-physical wave function. We will tackle this by defining our first quantum mechanical postulate (unproven good guesses):
While not actually a wave, the probability of finding an electron scales with the wave function's amplitude. While the amplitude is not a probability, because of this relation, it is possible to scale the wave function to give us some probability-like intuition of where the electron is. To do this, we need all probabilities to be real and positive (hence we take the magnitude squared of the imaginary wave function instead of just the plain wave function).
Given the first postulate, we have a few mathematical terms to get straighten out. First, the probability of finding the electron at all locations has to sum to 1. We call this normalization.
Given the first postulate, we have a few mathematical terms to get straighten out. First, the probability of finding the electron at all locations has to sum to 1. We call this normalization.
Where the star indicates the complex conjugate of psi(x).
Second, probability has no units. Hence the integral in equation 1 must have no units.
Second, probability has no units. Hence the integral in equation 1 must have no units.
Let us now check our first requirement with the plane wave solution to the wave equation. We need to check that the wave function normalizes to 1. We will ignore the time component for now (though we will bring it back later) because we discussed earlier that the position and time components are separable.
Unfortunately, this means that the general wave function does not normalize, which should have made sense as e^ikx is just a combination of sin and cosine, which never decay to zero at infinity. However, this is okay because our wave function does not have to be just e^ikx. It can be a superposition of tons of different e^ikx functions with different allowed k values (k is a function of some integer 'n'). And we know, from Fourier Series, that the sum of periodic waves can approximate almost any periodic function. This includes a periodic function that decays at x = +/- infinity (and hence a function that can be normalized). Really, e^ikx is just the basis (the irreducible form that can span the whole space of periodic functions). We can now write the correct (but still general) wave function form as so:
The wave function is a superposition of different basis states with some coefficient in front (to ensure that it normalizes). For those unfamiliar with the term basis: basis is the least number of vectors or functions needed to describe / superimpose any point in a system; the basis set for three dimensions is the x, y, and z unit vectors. They are not necessarily normalized, but the normalization constant is just a constant like C_n
Also note: I did not write the e^ikx basis set because, as we will see, sometimes the best basis set to describe a particle is not necessarily a plane wave (which we have shown has its own complications). I just wanted to be clear right now that whichever basis set I use, I will call it Phi. Phi will always be represented in its own normalized form such that its own square integral is 1. This is just by convention to make it easy. If this is confusing, just remember that we are only motivated to use the plane wave because of the experimental wave-like nature of particles, not because we proved it right for every system. It is a stepping stone, and considered the wave function of a free particle (most basic particle without any crazy potentials from other particles).
Either way, let us recheck our normalization, but for convenience, let us look at a two-basis set problem and generalize our way up.
Also note: I did not write the e^ikx basis set because, as we will see, sometimes the best basis set to describe a particle is not necessarily a plane wave (which we have shown has its own complications). I just wanted to be clear right now that whichever basis set I use, I will call it Phi. Phi will always be represented in its own normalized form such that its own square integral is 1. This is just by convention to make it easy. If this is confusing, just remember that we are only motivated to use the plane wave because of the experimental wave-like nature of particles, not because we proved it right for every system. It is a stepping stone, and considered the wave function of a free particle (most basic particle without any crazy potentials from other particles).
Either way, let us recheck our normalization, but for convenience, let us look at a two-basis set problem and generalize our way up.
To make sure everyone is following:
5: The definition of our wave function for this system (given)
6: Take the square integral of our wave function to make it normalized (to 1)
6 to 7: Expand the squared term
7 to 8: A basis set is defined to be orthogonal and hence the phi_1 and phi_-2 terms sum to 0.
8 to 9: our basis set is normalized, so they integrate to 1.
Equation 9 appears to be a sum of squares of constants that equal 1. This looks a lot like a probability (in fact it is derived from the initial psi^2 which we claimed was a probability). Hence, we extrapolate a second postulate:
5: The definition of our wave function for this system (given)
6: Take the square integral of our wave function to make it normalized (to 1)
6 to 7: Expand the squared term
7 to 8: A basis set is defined to be orthogonal and hence the phi_1 and phi_-2 terms sum to 0.
8 to 9: our basis set is normalized, so they integrate to 1.
Equation 9 appears to be a sum of squares of constants that equal 1. This looks a lot like a probability (in fact it is derived from the initial psi^2 which we claimed was a probability). Hence, we extrapolate a second postulate:
This leads us to a very important note. While the wave function basis can never change, the coefficients in front of each basis function only relates to the probability of being in the given basis state. This term can and does change. Let us consider a simple example. If there are two basis states 1 and 2, each with a 50 percent probability then we defined the wave function as a linear combination of the two (with a cofactor of 1/2). Now we measure the particle and find it in basis 1. Now, we are 100 % sure that we are in state 1 and not 2. Now the probability distribution changes such that the wave function is a linear combination of states 1 and 2 with the cofactor before 1 being 1 and the cofactor before 2 being 0.
As one may start to recognize … nothing on this page was proven, and all consist of experimentally motivates postulates (which you should always read as educated guesses). It is because of this very nature that quantum mechanics is very hard to interpret (what does a specific wave function for a particle really say about it??). Additionally, I should also note at this point that quantum mechanics is wrong. It has been disproven (see the hidden variable theorem). However, so is classical mechanics, but engineers use it every day to build skyscrapers. Quantum mechanics gives scientists a very good intuition about particles and their un-classical behavior but let us never forget our core assumptions in the model.
As one may start to recognize … nothing on this page was proven, and all consist of experimentally motivates postulates (which you should always read as educated guesses). It is because of this very nature that quantum mechanics is very hard to interpret (what does a specific wave function for a particle really say about it??). Additionally, I should also note at this point that quantum mechanics is wrong. It has been disproven (see the hidden variable theorem). However, so is classical mechanics, but engineers use it every day to build skyscrapers. Quantum mechanics gives scientists a very good intuition about particles and their un-classical behavior but let us never forget our core assumptions in the model.
|
|
|